All of these “parameters” are already present in Scrivener 3. What are you asking for that doesn’t already exist?
Scrivener’s compiler does do part of the processing (transferring semantic structure of the project), but if we assume you are referring to the “final visual product”, then yes.
Binder is amazing yes (plus the power of styles, which are BOTH abstract and visual scaffolding for words, unique among writing tools). But the compiler is doing way more than simply lining up docs. In my mind the compiler[1] is the biggest single feature that allows me to write in a semantic structure that can be parsed out to a huge range of visual outputs.
- I keep the Quarto/Pandoc metadata outside the “Draft” folder but then attach it as front-matter. Front/back-matter are useful adjuncts for structure (ScrivQ does amazing things here to generate Quarto YAML from binder items)…
- Custom metadata (stored not in the Binder but the Inspector) can also drive compiler features, so technically this is also sent to Quarto/Pandoc. For example you can use metadata to store quarto
#idor.classspecifiers that transform the Quarto layout. - More minor, but I keep all my figures in the Binder and these are exported, these are not technically text but the binder can manage multiple figures brilliantly… for example I make my figures in Adobe Illustrator that are stored in the binder, then export PNGs or SVGs that are kept as children to the AI, and these are then linked into the draft docs and exported.
- I’m sure you could use notes / annotations etc. for content if you wanted, but at least i don’t.
Yep, this is why I love Scrivener. Note that Scrivener’s compiler does more than the “starting point”, it generates an almost fully formed complex document that only requires some minor post-processing (which Scrivener can also orchestrate). My post-processor makes any changes, then runs Quarto/Pandoc directly, so a single keypress in Scrivener orchestrates a full workflow to final visual product without further ado…
If I could dictate what I wanted in Scrivener 4 for Academic users:
- Bundle Pandoc, thus allowing citeproc (the bibliography engine built-in to Pandoc), to generate Bibliographies in any Scrivener compiler output.
- Use the user’s shell session (the .zshrc / .bashrc settings) for post-processing. This stops bootstrapping scripts like mine from being needed.
- Have “export files” in the compiler, so we can store accessory files like CSL or templates in the binder and then selectively export them to the current compile folder at compile time automatically. This enables Scrivener to automagically set up a destination folder with required files. Different compile formats could export different templates etc.
- Better tables, Pandoc now supports more complex table features and Scrivener should be able to drive them.
- More nuance in how text is transformed. An example being the suggestion from @amberV about {properties} placement.
- Possibly have replacements that could be toggled to work before and after the markup is generated. This would be a single
 ︎ to toggle this in the GUI.
︎ to toggle this in the GUI.
I’ll leave it there…
[1] the compiler + the binder are synergistic more precisely, it is hard to really just say one feature alone is the main workhorse…
Scrivener 3 is amazing! But there are some friction points for academic/technical writing, which often uses Markdown and LaTeX and gets processed via Quarto or Pandoc. My hope in this thread is to distill it down into a clear DAG so we can develop a robust way of using these tools together. In some cases, no changes will be needed in Scrivener, but maybe we figure out a better way of using Scrivener. In other cases, we may pinpoint a difficult challenge for which adding a feature in Scrivener 4 would be the best (or only) solution. The goal is to be able to describe this very specifically to the Scrivener developers, ideally to make adding such a thing feasible. We are trying to go beyond simply saying “please add better Markdown support,” which doesn’t really help. Especially with the New Simpler App being developed (and likely having some code back ported into Big Scrivener), this type of brainstorming may end up being helpful.
That’s fine. I understand. But the post I was responding to simply describes existing Scrivener 3 capabilities.
I worry about keeping metadata that is meant to be sent to Quarto/Pandoc hidden in the nooks and crannies of the Scrivener interface. My thought is that if something is meant to go to Quarto/Pandoc, then it should be in the Binder text documents somehow.
My thought is that Scrivener’s other tools would be used to help the writer within Scrivener, during the writing process itself. For example, notes to self, summaries, bookmarks, status labels, etc. It is analogous to storing reference material in the Binder, but this would not get included in the export.
Storing Quarto/Pandoc-specific metadata in various parts of Scrivener’s interface may risk incompatibility in the future (if, for example, Scrivener 4’s interface changes), or may just be harder for the writer to keep track of.
Certainly, there are pros and cons to each approach though.
Yes, this seems like a powerful workflow that keeps everything within the Scrivener file bundle, rather than managing a folder of external assets.
When you link to a specific file format (child object), how do you accomplish that in Scrivener?
And what happens behind the scenes during Compilation and Processing?
If you want to, you can certainly put it there.
Scrivener is unlikely to ever produce Markdown output exclusively, so it’s likely to continue to give users the flexibility to put their metadata wherever is most convenient for them.
Yes, all your suggestions are golden. I think the Shell is a big one.
The Inspector isn’t a nook or cranny, it is a core part of the UI that is not going anywhere as much as i can predict these things… I could embed the metadata in the text itself, and Scrivener is great in that there are several ways to do things. But custom metadata really makes the workflow smoother, it is document specific yet stays out of your way during writing.
I drag a figure into the editor. I have Scrivener set up so that it links not embeds the image.
Therefore I can edit the image in the binder and any place it was linked also updates. The slight wrinkle here is that the binder stores the files, and so you have to use Scrivener to edit them externally and save back to the same files:
“Replace Media file…” is also useful here. I use mouse gestures using BeterTouchTool so I gesture over a binder image and “Replace Media file…” runs on that item (you could bind a keypress for that, but i like gestures)…
Thanks. But when Scrivener compiles to Markdown, does that internal link become the standard Markdown that Pandoc/Quarto expects, , with the image being stored within the compilation folder as test_figure.png?
I’m wondering about the intermediary steps between .scriv > .md (.qmd) > Pandoc/Quarto processing.
And how would Scrivener manage parameters attached to the link such as size or placement – for example, what would you do in Scrivener to have it output the Markdown {fig-align="left" width=4in} or adding a cross-ref like {#test-fig}? (I believe these are the nuances that you and AmberV were talking about earlier in the thread, and perhaps what your Ruby script helps to take care of.)
Yes ![]() . Technically, Scrivener converts linked or embedded images to markdown reference links:
. Technically, Scrivener converts linked or embedded images to markdown reference links:
![A Caption comes from a paragraph styled with the caption style that follows an image in the editor][ImageID]
…
[ImageID]: image.png {width=720 height=391}
Markdown captions are generated from the caption style, and width and height properties can be generated using a resize dialog from the context menu for the image in the editor. The image is exported with the name specified in the binder, you don’t need to worry about any of this, it is all handled automagically by Scrivener: drag-n-drop an image, write a caption and Scrivener handles the naming and markup.
From above you see there are no real intermediaries for basic function.
One problem I’ve faced however is that Scrivener’s width and height can conflict with layout in some formats (Typst for example which cannot use unitless values). In these cases I run a regex that removes the dimension attributes in my post-processor, e.g. scrivomatic/quarto-run.rb at master · iandol/scrivomatic · GitHub
This is exactly the problem with pandoc-crossref and Quarto cross-references: they use the #id attribute but how do you get the label into the reference link. The label will be somewhere close to the image markup, I prefer to write my labels inside the caption for example, but Scrivener will put attributes at the end of the document:
![#fig-test ⇦ I put my label in the caption, but pandoc-crossref or quarto need it in the {attributes} all the way at the bottom of my document ↓][ImageID]
…
[ImageID]: image.png {ID SHOULD BE HERE width=720 height=391}
My script takes that markdown and rewrites it to put the label in the right place, thus cross-refs now work fine. The same mechanism that I use for crossref labels can be used for any other attributes.
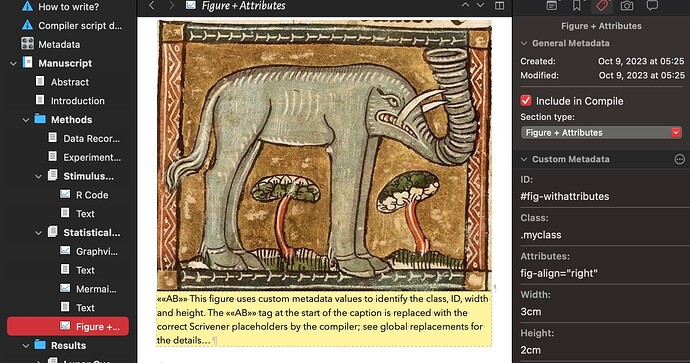
As a worked example: If you make use of section types, metadata and replacements, then attributes can be stored in the inspector. My Quarto sample project demonstrates how this works. Here is a document which will become a Quarto figure with custom attributes in the output .qmd, note the Inspector values:
I use a temporary marker in the caption ««AB»», the compiler replaces this label with the values you enter in the inspector:
…becoming this raw markup from Scrivener:
![{#fig-withattributes .myclass fig-align="right" width=3cm height=2cm} This figure uses custom metadata values to identify the class, ID, width and height. The ««AB»» tag at the start of the caption is replaced with the correct Scrivener placeholders by the compiler; see global replacements for the details…][Elephant3-1]
…
[Elephant3-1]: Elephant3.jpg
This will of course fail in Pandoc or Quarto as the attributes shouldn’t be inside the caption; because Scrivener uses ref links they need to be moved out of the caption and to the bottom of the doc, so my post-processor script rewrites the markdown to:
![ This figure uses custom metadata values to identify the class, ID, width and height. The ««AB»» tag at the start of the caption is replaced with the correct Scrivener placeholders by the compiler; see global replacements for the details…][Elephant3-1]
…
[Elephant3-1]: Elephant3.jpg {#fig-withattributes .myclass fig-align="right" width=3cm height=2cm}
When Scrivener 3 was in beta, we never specifically envisaged Quarto would come along years later and need attributes injected. Honestly, the fact we have a flexible UI to control arbitrary attributes for any piece of content is a testament to how well designed Scrivener’s compiler architecture is. Better control of attribute placement could be improved in Scr4 (what @AmberV and i were discussing, using inline links would make the regex simpler, or some smarter heuristics as suggested by @AmberV would negate the need for post-processing), but this is still a great workflow in Scr3.
Thanks for your kind and thorough response. It was very clear, and I understand now.
Your sample project actually demonstrates three alternative writing workflows:
- writing Markdown/LaTeX directly in the editor
- using Styles to simplify markup, injecting customized metadata as the parameters where needed
- using Section Styles to essentially wrap that document in a
divblock; perhaps most important to allow for nesting of a Style within a Section Style block.
You’re right that the fact that any of this is possible is testament to the forward-thinking ingenuity of KB and the Scrivener development team, beta testers, et al.
Update:
For the last several days, I’ve been slaving away at a different approach toward integrating Scrivener with Quarto. Briefly,
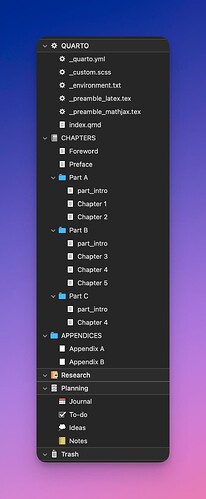
- I am able to construct the outline of my Quarto Book project using the Binder.
- I use Scrivener’s Editor window to write each document, using Markdown with Styles only supplying visual gloss to ease readability.
- I wrote a Python program (that I named Squarto) that explores the
.scrivproject package, identifies the.scrivxXML document within it, and identifies the/Files/Data/directories. - Squarto discerns the Binder organization from the
.scrivxfile, slugifies all the titles, creates the folder and file hierarchy on the computer, copies over the source files (content.rtf, content.png, etc.), also converting.rtfto plain text format, renaming each document with Quarto’s.qmdsuffix, etc. - Finally, the program constructs the appropriate YAML to tell Quarto all about the chapters, parts, and appendices in the project. This YAML then gets inserted dynamically into the
_quarto.ymlfile. This part is very flexible and can many different setups for Quarto Book projects. - While Scrivener is not used to compile the project (Squarto takes care of the export/compilation itself), nevertheless Squarto looks to see whether Scrivener has marked a folder/file in the DraftFolder as “IncludeInCompile.” This is a handy way to tell Squarto to only export/compile selected chapters.[1]
At the end of this sequence, the quarto render command is executed in the Bash shell to build the project. Since at this point, it is Quarto (and Pandoc and LaTeX and Jupyter) doing all the work, all the Quarto features are available (e.g., code, figures, citations, tables, etc.).
Here is a quick snapshot of the Scrivener project:
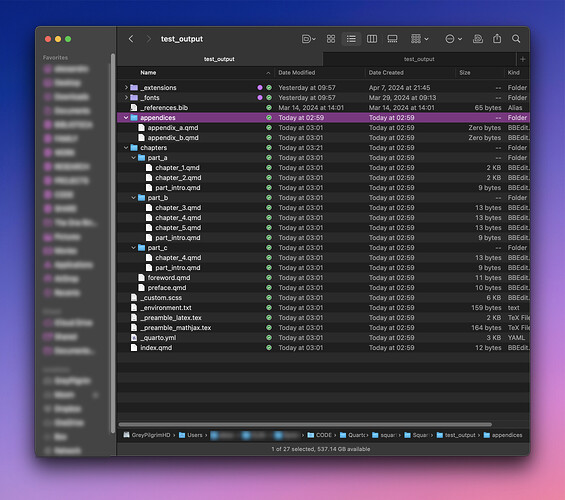
When executed, here is the Finder window showing the directories:
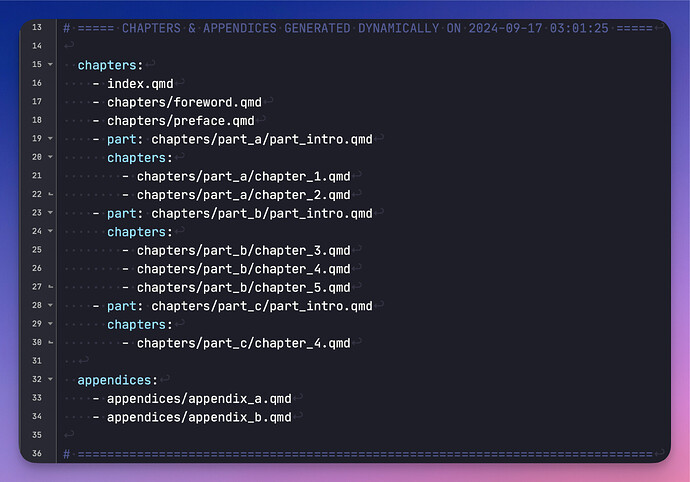
And here is a closeup of the YAML that gets auto-generated:
I’m not gonna lie… This took me forever, due to idiosyncrasies of both Quarto and Scrivener. But overall, it shows the extremely well-thought-out structure of the .scriv project bundle and the .scrivx XML document.
There are some additional features that I’d like to work on, such as combining stacked text documents from the Binder into one chapter .qmd file. Also, while I can link to figures (images) using Markdown, and I can reference that figure in the “Figures” folder in the Binder (not shown in the screenshots), the figure does not appear at the location of the link/crossref. It would be nice to figure out how to make that work. Presently, I manually moved over my bibliography file (symlink), fonts, and Quarto extensions into that directory. While it might be possible to embed them within the Scrivener document, I’m actually thinking of using Cookiecutter to set up the base directory from a template, in which case all the necessary files will be there automatically. Finally, the Squarto program right now is specific to a Quarto Book project. It would be nice to add flexibility to support Quarto Manuscript projects (which are simpler anyway!).
Overall, I’m pretty pleased with this test document. Next, I will copy over the textbook that I’ve been working on, and I’ll see if I run into any trouble. (I’m expecting something to pop up as soon as I am dealing with more finicky LaTeX details.)
(Unfortunately, Scrivener is limited here in its ability to Compile things outside of DraftFolder/Frontmatter/Backmatter. In the Binder representing the Quarto Book project, things like Quarto config settings, Appendices, Figures are all regular folders outside the DraftFolder, and these cannot be marked to include/exclude via the Compile settings window; thus they are all exported/compiled by Squarto.) ↩︎
Make sure you have good backups. Using other software to poke around inside a Scrivener project is unsupported and entirely at your own risk.
Thanks for the warning. The program only copies stuff out of the Scrivener project file. It doesn’t write anything in there. So it is similar to exploring the package contents in the Finder.
I think it is important for L&L to remind us that poking around the project bundle is not supported, having said that it is also clear that KB did a great job of making the scrivener format as open and discoverable as possible given the choice of very logically structured XML etc. I think it is great that we have this incredible flexibility, and your solution fits this path well.
I’m curious though on the thought process choosing to build your own compiler rather than just making a simpler splitter script? I assume you are happy explicitly writing all the necessary markdown into the editor directly, but arguably you are losing many of the other structural benefits (separation of concerns, semantics vs. stylistics) that Scrivener-features⇨markdown (lists, simple tables, figures with captions etc) + Section Types + Block/Inline Styles afford?
Now your cool sounding Squarto could definitely make use of Section Type metadata as they are contained in the XML to inject bespoke markup, but Styles utilise some custom RTF tags that I think no other RTF library supports. And as you mention, you also seem to break the ability to drag images into the editor and auto-link+export named image files?
Well, one reason that I created Squarto is because I wanted a workflow that incorporated exportation[1] and Quarto-specific compiling[2] of the project into a fully functional Quarto Book project (all folders and files hierarchically organized, all filenames slugified, the YAML being dynamically populated with the paths for the chapters, parts, and appendices, and automatically injected into the _quarto.yml file, etc. It’s all rather clean and satisfying, actually!) Having the actual Quarto Book project was important for versioning (git) and for sharing with colleagues. With the other existing Scrivener/Quarto workflows, I had a Scrivener project that could produce my .PDF or .docx document, maybe even an aggregated Markdown intermediate artifact, but not the actual “canonical” Quarto Book project itself.
Squarto can be set to run every time the Scrivener project is saved. This updates the Quarto Book file structure, and in turn, should update the quarto preview web server, too. (I haven’t tested live updates yet, but quarto preview works great on a freshly compiled Quarto Book.) Since I write in Markdown, I can also use Marked2 to give me a quick side-by-side preview as I’m writing. With the other existing Scrivener/Quarto workflows using Styles, I couldn’t figure out how to get a helpful preview.
But perhaps the biggest reasons to do this were to learn more about how Scrivener works “on the inside” and to have a challenging project to tackle in Python! (Most everybody loves to crack a nut sometimes.)
Back to our wish list for Scrivener 4: if the Compiler were to have more of a DAG (directed acyclic graph) type of workflow – do step 1, then step 2, then step 3 – I think it would be versatile enough to accomplish everything that Squarto does through a series of Scrivener functions plus customized scripts.
Scrivener has an export function, but it is not integrated into the Compiler. Scrivener’s export is of the contents of the Binder, but it is not a functioning Quarto Book project. ↩︎
Scrivener’s Compiler is designed to deal with the DraftFolder, but many other crucial bits of a Quarto Book project are outside the DraftFolder in other Folders. Scrivener wasn’t designed to treat these other Folders in the same way as DraftFolder. ↩︎
![]()
yup, I find I learn more when there is a clear problem to solve rather than some abstract, “…suppose I should learn Python at some point…”
Right, those other projects have post-processing scripts that go directly to output, but that is not required. You can use a splitter-script FIRST to take the single markdown generated by Scrivener’s compiler, split based on parts/chapters and build the Quarto Book project from there (i.e., instead of reading the .scrivx to get parts and chapters, you read and use the headings in the markdown itself). This would both take advantage of Scrivener’s compile toolset, and still get you a full folder structure of [sub]folders and files.
BTW, my third item in my wishlist post above “Have “export files” in the compiler” would allow us to store and build up the accessory files for a workflow like yours. You could keep YAML, BIB, CSL, template files as Binder items (even better if they were softlinks) and they would be copied out to the [sub]folder every time the compiler ran… Like a simple file orchestrator…
This is a very nice idea, also.
As it stands, Squarto will create the folders and files as they exist in the binder. I like this because it is so visual. If you rearrange the binder, then Squarto will rearrange the folders/files accordingly, and the YAML is auto-generated accordingly. So the user only needs to worry about the binder.
I like your suggestion… But thinking aloud, were the “splitting algorithm” that you suggest to look for Markdown headings to decide file splits, then the ordering might differ from that in the binder depending on whether a document in the binder have one heading, multiple headings, or even zero headings.
Maybe a hybrid approach is (1) to do what I’m doing already in analyzing the .scrivx XML binder structure to set up the folders; but (2) instead of grabbing the content.rtf directly from /Files/Data, I would read the subsection of content from the Compiled Markdown and save it as the .qmd file in the location specified by the binder. That ensures that the binder continue to serve as the “user interface” to defining structure, but the Scrivener Compiler would handle conversion to Markdown like in Scrivomatic and ScrivQ. In this case, all of your other tricks for Styles and figure captions, etc., could still be utilized.
It’s a thought!
Until Scrivener adds “export-this-file-to-this-directory” functionality to the Compiler, then I have to rely on Squarto to do that heavy lifting. Right now, I have stored Quarto configuration files like _quarto.yml, .css, and .tex in the Binder, and Squarto will export it to the right place. But I added my .bib and .csl files, fonts, and the Quarto extensions myself. I will work on implementing a Cookiecutter method so that the initial step of the Squarto workflow will be to instantiate a Cookiecutter template that already contains these supporting files.
I don’t mind writing in Quarto Markdown. But I admit that I hate re-reading Markdown, especially tables and equations.
At least it’s better than re-reading LaTeX ![]()
LOL.